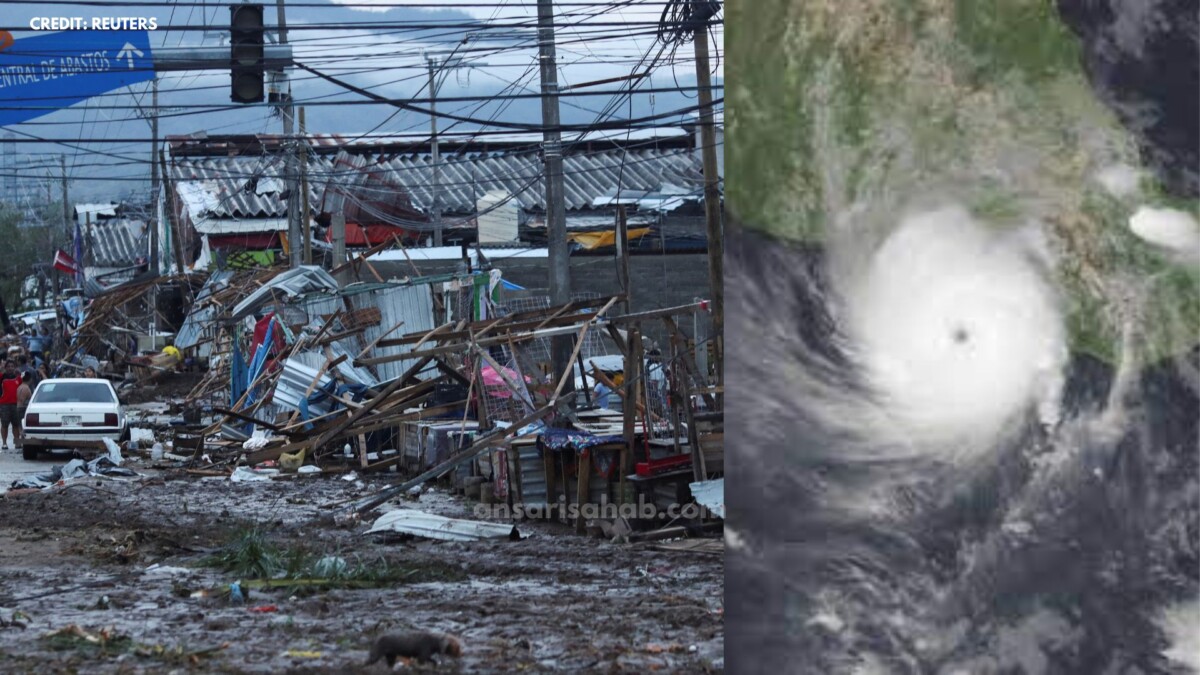
On October 26, 2023, Hurricane Otis, a catastrophic Category 5 storm, made landfall in Acapulco, Mexico. The rapid intensification of this hurricane, which strengthened from a Category 1 to a Category 5 in just 24 hours, has raised concerns about the growing threat of extreme weather events due to climate change. In this blog, we will delve into the impact of Hurricane Otis, the factors contributing to rapid intensification, and the urgent need for climate resilience to protect coastal communities.
The Impact of Hurricane Otis
The devastation caused by Hurricane Otis was immense. The storm brought sustained winds of up to 165 miles per hour and storm surges as high as 20 feet, resulting in widespread damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure in Acapulco. The consequences were severe, including:
- Loss of Life: At least 100 lives were lost, and many more people remain missing. The death toll is expected to rise.
- Homelessness: An estimated 10,000 people were left homeless as their homes were either destroyed or rendered uninhabitable.
- Infrastructure Damage: Power outages, flooded roads, and damaged bridges disrupted daily life and transportation networks.
- Economic Impact: The storm caused an estimated $10 billion in damages, with significant repercussions on the local economy.
The Aftermath of Hurricane Otis
In the wake of Hurricane Otis, Acapulco is struggling to recover. While the Mexican government has deployed thousands of troops and emergency workers to aid in relief efforts, the scale of destruction is immense, and recovery will be a long and challenging process.
Rapid Intensification: A Growing Concern
The rapid intensification of Hurricane Otis is a grave reminder of the escalating threat of extreme weather events, driven by climate change. Rapid intensification, a phenomenon wherein a hurricane’s wind speed increases by at least 35 knots within a day, is becoming more frequent. Scientists point to factors such as warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and high air moisture as contributors to rapid intensification.
Climate Change and Rapid Intensification
Climate change plays a pivotal role in the increasing frequency and intensity of rapid intensification. It leads to the warming of oceans, providing more energy for hurricanes to form and strengthen. This warming effect heightens the risk of more powerful and dangerous storms like Hurricane Otis.
Read Also: Andhra Pradesh Train Accident: 9 Killed, 40 Injured, Human Error Blamed
Reducing the Risk of Future Storms
To mitigate the risks associated with rapidly intensifying hurricanes, various measures need to be taken:
- Coastal Defenses: Investment in coastal defenses like seawalls and levees is crucial to protect communities from storm surges.
- Early Warning Systems: Enhancing early warning systems provides residents with more time to prepare for impending storms, potentially saving lives.
- Resilient Infrastructure: Building resilient infrastructure that can withstand high winds and flooding is essential for reducing damage and aiding recovery efforts.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is vital to mitigate climate change and slow the warming of the ocean.
The Future of Hurricanes
The future of hurricanes is uncertain, but one thing is clear: we need to take decisive action to protect our communities from the increasing threat of rapidly intensifying storms. As the consequences of climate change become more pronounced, we must adapt and strengthen our resilience.
Conclusion
Hurricane Otis was a catastrophic event that left a trail of destruction in Acapulco, Mexico. The rapid intensification of this storm is a stark reminder of the growing threat posed by climate change, which is causing hurricanes to become more intense and frequent. To reduce the risk of future storms and protect coastal communities, we must invest in resilient infrastructure, early warning systems, and efforts to mitigate climate change. The time for action is now.
Additional Information
Here is additional information about Hurricane Otis and its impact:
- Hurricane Otis was the most powerful hurricane to hit the Pacific coast of Mexico since Hurricane Patricia in 2015.
- Rapid intensification is a rare but dangerous phenomenon that can lead to very powerful and destructive storms.
- Scientists believe that a combination of factors, including warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and high air moisture, can contribute to the process of rapid intensification.
- Climate change is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of rapid intensification, as it is causing the ocean to warm.
- The Mexican government estimates that the cost of rebuilding Acapulco after Hurricane Otis could reach billions of dollars.
The devastation caused by Hurricane Otis serves as a poignant reminder of the need for global cooperation in addressing climate change and building climate resilience to protect vulnerable communities.