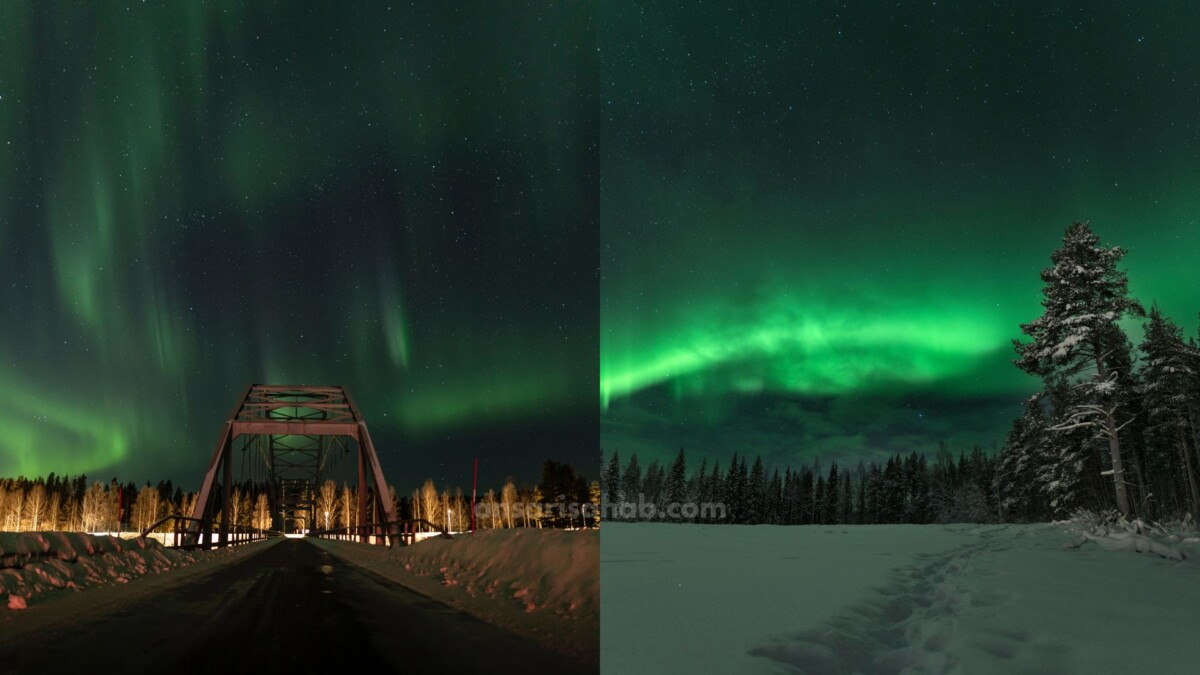
As we celebrate the one-year mark of our solar journey, the sun has gifted us a mesmerizing celestial event—an impending display of the Northern Lights, also known as the Aurora Borealis. A recent solar eruption has set the stage for a geomagnetic storm, sparking the hopes of witnessing this ethereal phenomenon in the northern United States. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the science behind geomagnetic storms, the potential visibility of the Northern Lights across lower latitudes, and practical tips for optimizing your chances of experiencing this breathtaking natural spectacle.
Understanding Geomagnetic Storms and Their Impact:
Geomagnetic storms are temporary disruptions in Earth’s magnetic field caused by charged particles from the sun colliding with our magnetosphere. The intensity of these storms is measured on a scale ranging from G1 (Minor) to G5 (Severe), with the current watch indicating a G2 (Moderate) storm. These storms can lead to the Northern Lights becoming visible at latitudes not typically associated with this celestial display.
The Dance of the Northern Lights:
The Northern Lights result from the interaction of solar particles with Earth’s atmosphere, creating a stunning luminous dance in the night sky. While traditionally confined to high-latitude regions like the Arctic Circle, strong geomagnetic storms can extend their reach to lower latitudes. The upcoming storm, expected from November 29 to December 1, 2023, holds the promise of illuminating states such as Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and New York with this celestial spectacle.
Tips for Optimal Northern Lights Viewing:
- Check the Geomagnetic Storm Forecast: Stay informed with real-time forecasts provided by the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) to gauge the likelihood of Northern Lights visibility in your area.
- Find a Dark Location: Escape the glare of city lights and head to rural areas or parks with minimal light pollution for an unobstructed view of the celestial show.
- Look North: The Northern Lights typically manifest in the northern sky, so position yourself facing north for the best chances of witnessing the display.
- Be Patient: Aurorae can be unpredictable, so exercise patience and give yourself ample time to marvel at nature’s light show.
Suggested: Solar Superstorm Threat Could Wipe Out the Internet: What you need to know
Potential Visibility Across the Northern US:
The geomagnetic storm watch suggests that the Northern Lights could be visible as far south as Pennsylvania, Iowa, Nebraska, and Colorado during the specified period. To maximize your chances, plan your viewing session during the night, ensuring you’re away from city lights and under clear skies.
Additional Information:
- Nature’s Light Symphony: The Northern Lights are a result of charged particles from the sun interacting with Earth’s atmosphere, creating a dazzling display of colors.
- Geomagnetic Storm Causes: Solar eruptions, such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), trigger geomagnetic storms that influence the intensity of the Northern Lights.
- Severity Scale: Geomagnetic storms are classified on a scale from G1 to G5, with G5 being the most severe and capable of producing the most vibrant auroral displays.
- Technological Impacts: Geomagnetic storms can affect human technology, causing disruptions to satellite communications and power grids.
Conclusion:
As we mark the first anniversary of our solar journey, nature presents us with a celestial gift—the potential to witness the Northern Lights in the northern United States. Armed with knowledge and these practical tips, venture into the night, embrace the chill, and gaze northward for a chance to be captivated by the enchanting dance of the Aurora Borealis.
Additional Information:
- Global Visibility: While the Northern Lights are commonly seen in the Arctic and Antarctic regions, strong geomagnetic storms can extend visibility to lower latitudes.
- Technological Disruptions: Geomagnetic storms can impact power grids and communication systems, highlighting the interconnectedness of Earth and the sun.
- Auroral Oval: The Northern Lights are typically visible in the auroral oval, a ring-shaped region around Earth’s magnetic poles.
- Solar Cycle Strength: The recent geomagnetic storm is the strongest of the current solar cycle, promising a particularly spectacular display of the Northern Lights.
By following this guide and immersing yourself in the magic of the night sky, you’re poised to witness one of the most captivating and awe-inspiring displays nature has to offer—the Northern Lights in the northern United States.